New membrane catches CO2
An inexpensive and eco-friendly plastic membrane separates CO2 from other gases.
Approximately one third of the total carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in the world come from energy production. CO2-free gas-powered plants are based on carbon dioxide being removed from the waste gases and deposited underground.
However, before CO2 can be stored, it must be separated from the waste gases. The current methods used for this type of filtration are expensive and require the use of chemicals. A new membrane technology will change that.
A new type of membrane has been internationally patented by researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) in Trondheim. The membrane is made from a plastic material that has been structured using nanotechnology. It catches CO2 while other waste gases pass freely.
The technology is effective, inexpensive and eco-friendly, and can be used for practically all types of CO2 removal from other gases. Its effectiveness increases proportionally to the concentration of CO2 in the gas.
Copying lungs
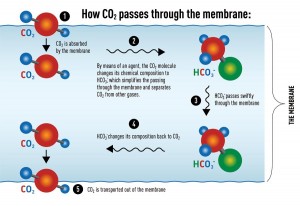
This method is called “facilitated transport” and is comparable to the way our lungs get rid of CO2 when we breathe: it is a complex but effective mechanism.
“The novelty is that instead of using a filter that directly separates CO2 and other molecules, we use a so-called agent. It is a fixed carrier in the membrane that helps to convert the gas we want to remove,” says NTNU Professor May-Britt Hägg. She is head of the research group Memfo that works on the new membrane technology.
The agent helps so that the CO2 molecules in combination with moisture form the chemical formula HCO3- (bicarbonate), which is then quickly transported through the membrane. In this manner, the CO2 is released while the other gases are retained by the membrane.
Nanoplastic
Various materials are used to make membranes. It could be plastic, carbon and/or ceramic materials. Membrane separation of gases is a highly complex process. The materials must be tailored in an advanced way to be adapted to separate specific gases. They must be long-lasting and stable.
The new membrane is made of plastic, structured by means of nanotechnology to function according to the intention. Membranes based on nano-structured materials are eco-friendly and will reduce the costs of CO2 capture.
“With this method, we can remove more CO2 from gas streams and obtain a cleaner product. Thus, it becomes less expensive,” Hägg says.
“We also have membranes today that are used to separate CO2 and have been used for a couple of decades, but these membranes are used for natural gases at high pressures, and are not suited for CO2 from flue gas. If the membrane separated poorly, very large amounts of the material will be needed, and that makes this separation expensive,” Professor Hägg explains.
Membranes have a major potential to become an inexpensive and eco-friendly alternative in the future. An international patent has been taken out for the new type. Manufacturers both in Europe and the USA have taken an interest in putting it into production, the professor reveals.
Testing in Europe
About two years ago Memfo joined a consortium of 26 European businesses and institutions within a project named NanoGloWa – Nanostructured Membranes against Global Warming. The consortium has received EUR 13 million to develop such membranes. One of these millions is reserved for Memfo.
According to Hägg, the new technology ought to be very interesting for coal-powered plants. “Within a five-year period, the plan is to test the membrane technology in four large power plants in Europe. We believe this will result in an international breakthrough for energy-efficient CO2 membranes,” she says.
When it comes to gas-powered plants, the concentration of CO2 is so low that the pressure in the waste gas must be increased before the gas can be cleaned with this method. However, Professor Hägg reveals that StatoilHydro is currently developing a method for pressurized exhaust gas that could be combined with this membrane technology, and that would make it interesting for CO2 capture in gas-powered plants as well.
Besides CO2 purification in energy production, the method could be used for more or less any type of purification where carbon dioxide is removed from other gases.
“For instance, we are testing this method to purify CO2 from laughing gas in hospitals; a very interesting potential application,” concludes Professor May-Britt Hägg.
By Tore Oksholen