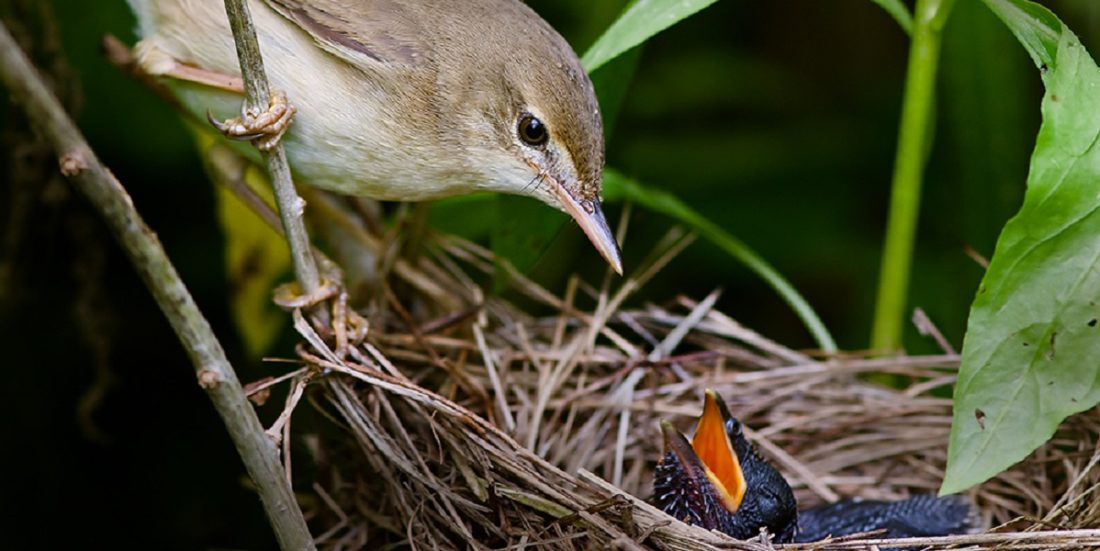
Why some cuckoos have blue eggs
Cuckoo eggs come in a wide variety of colours and patterns, but why?
EVOLUTION: For roughly a century, researchers have been trying to figure out how different female cuckoos manage to lay such a variety of different egg colours that match different host birds. Now, a group of researchers at NTNU has come up with an answer to this puzzle, in cooperation with researchers from all over Europe and Asia.
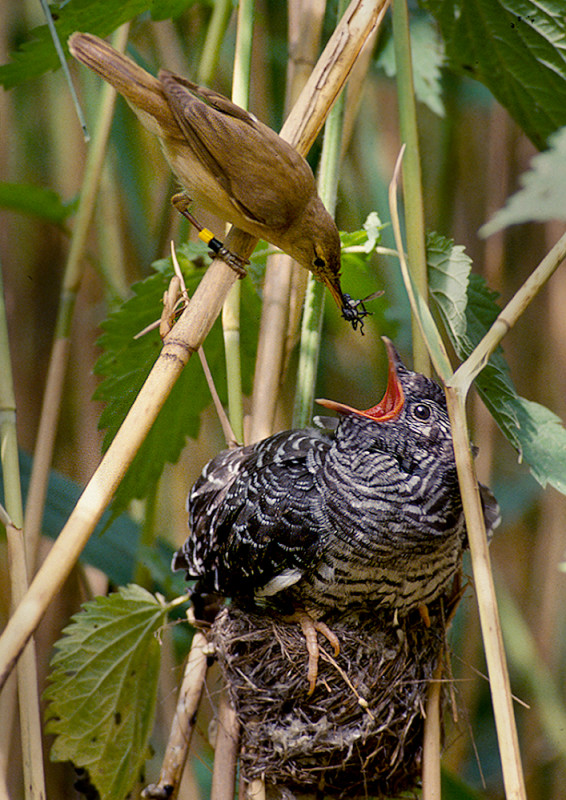

This reed warbler suddenly has a big mouth to feed. But its own offspring are nowhere to be seen. Photo: Per Harald Olsen, NTNU
The short answer is that “the female bird decides everything,” says researcher Frode Fossøy.
Fossøy is part of the cuckoo research group at the Department of Biology at NTNU. The results of the group’s work have just been published in Nature Communications1.
“We’ve been able to show for the first time that the blue egg colour is inherited via the female cuckoo only. The father has no effect on the colour of his daughter’s eggs,” says Fossøy.
Researchers have investigated a wide variety of samples from Europe and Asia. They found a clear relation between blue eggs and genetic material that only comes from the mother (mitochondrial DNA), and no relation between egg colour and genetic material that comes from both parents (nuclear DNA).
- You might also like: How do small birds survive the winter?
Females are specialists on one host species
Cuckoos (Cuculus canorus) are parasitic. Female cuckoos lay their eggs in the nests of other bird species, as is well known.
The young cuckoo then usually throws the other chicks out of the nest, getting rid of any competition for the parents’ attention.
Potential host birds develop traits to prevent being tricked by the parasites—they get rid of eggs that don’t look like their own. To avoid this, female cuckoos need to lay eggs that look identical to that of the host bird’s, both in colour and shape. This means that there is a sort of evolutionary arms-race going on between cuckoos and host birds, where cuckoo eggs come to resemble that of their host birds’ more and more over time.
Different cuckoos can therefore lay eggs of many different colours and patterns. They can be blue, brown, green or grey, and have different combinations of spots and patterns. But each individual female cuckoo can only lay eggs in one colour, so different females specialize on different host species. This is part of the reason why egg colour is a trait inherited only from the female birds.
Story continues under the photo.

This illustration shows the wide variety of colours and patterns in eggs laid by cuckoos. Cuckoo eggs may be slightly different in size to a host bird’s eggs, but otherwise it is almost impossible to tell the difference, especially for humans. Illustration: NTNU
Males may make a mess of things
The research group doesn’t have definitive proof that all egg characteristics are inherited from the female bird, just that blue eggs are. Whether other egg colours also are inherited via females only is currently not known.
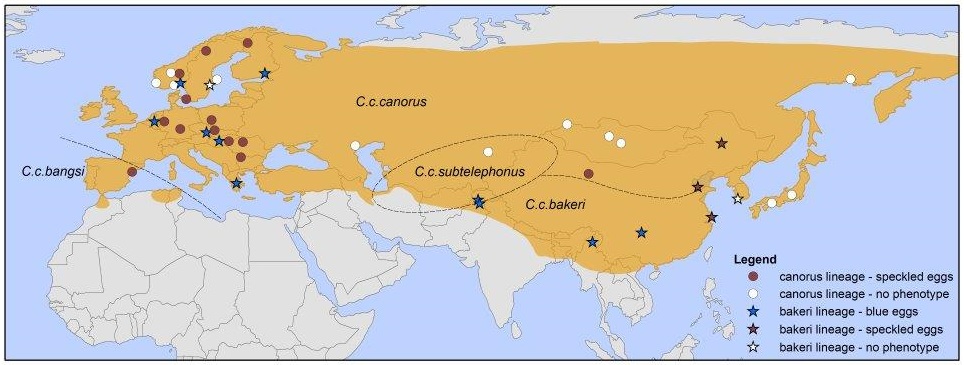
Cuckoos are found throughout Europe and Asia. There are four subspecies, mostly as a result of geographical spread. But interspecies breeding can happen, given the chance. Illustration: NTNU
There has been speculation that cuckoos that lay blue eggs may actually be a different species, but no other characteristics indicate this. The nuclear DNA of the birds that lay blue eggs is the same as any other cuckoo — meaning the species is the same.
A single male cuckoo can mate with several female birds that lay eggs of different colours. This could make a mess of things. If a male with genes for one colour mated with a female with a different egg colour, their daughter’s eggs could be an intermediate colour that doesn’t match any host, meaning that host birds would be able to spot the difference and get rid of the parasitic egg.
For this reason, there are evolutionary advantages for both the male and female birds that only females carry the genetic trait for egg colour. That way, their offspring will have a much greater chance of surviving.
Sex chromosomes
Egg colour traits are therefore most likely connected to the bird’s sex chromosomes. In birds, that is the W and Z chromosomes (similar to X and Y in mammals).

Cuckoo chicks gobble up all the resources that its host parents otherwise would use on their own offspring. Photo: Per Harald Olsen, NTNU
Male birds have a ZZ chromosome pair, while females have a ZW pair. In other words, only female birds have W chromosomes. Thus, if the gene for blue egg colour is located on the W chromosome, this gene will be inherited unchanged from mother to daughter.
Another possibility is that egg colour is connected to mitochondrial DNA, or mtDNA, which is also inherited only from the mother.
100 per cent certainty
Using a massive data set, including data from museum eggs that are over 100 years old, the researchers have been able to conclude with 100 per cent certainty that blue egg colour is inherited solely from the mother.
As a biologist, it isn’t often you can come to a conclusion with 100 per cent certainty. But this is an exception.
- You might also like: Searching for answers to a century-old biological question
Spread from Asia
The researchers’ results have mainly come from Finland, and cuckoos that lay eggs in redstart (Phoenicurus phoenicurus) nests, as well as material from blue eggs in China.
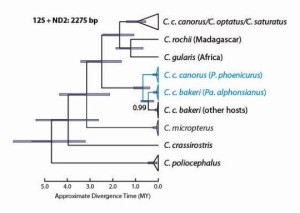
This illustration shows the connection between common cuckoos and related species, as well as subspecies. The subspecies marked in blue lay blue eggs. These birds split away about 2.6 million years ago. Illustration: NTNU
The blue egg colour has most likely originated in Asia.
“It happened about 2.6 million years ago,” Fossøy explains.
This trait was developed so long ago that four new species of cuckoos have evolved after blue eggs appeared. The blue egg trait thereby spread from Asia west to Europe, as female birds mated with local males and found local hosts to trick with their blue eggs. Because blue eggs are inherited only from female birds, this geographic spread hasn’t affected egg colour.
More work ahead
Just a few years ago, Fossøy published a study of three species of cuckoos in Bulgaria that indicated that male birds could affect egg colours2. While the trait for blue eggs is certainly only inherited from female birds, this may not be the case for other colours.
Eivin Røskaft, Arne Moksnes and Bård Gunnar Stokke all work with Fossøy and the cuckoo research group at the Department of Biology.
Other researchers who have contributed are Torbjørn Ekrem from the NTNU University Museum, Michael D. Sorenson, Wei Liang, Anders P. Møller, Jarkko Rutila, Fugo Takasu and Canchao Yang.
The research group now has the complete genome sequence of 50 cuckoos to sort through. Each individual has 1.1 billion base pairs in its DNA, which should give them more than enough to do.
Sources:
1. Fossøy, F. et al. “Ancient origin and maternal inheritance of blue cuckoo eggs”. Nature Communications 6:10272 doi: 10.1038/ncomms10272.
2. Fossøy, F. et al. (2011). “Genetic differentiation among sympatric cuckoo host races: males matter”. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 278(1712): 1639-1645.