Why you should care about better fibre optics
Fibre optic research can give us better medical equipment, improved environmental monitoring, more media channels – and maybe better solar panels.
“Optical fibres are remarkably good at transmitting signals without much loss in the transfer,” says Professor Ursula Gibson at NTNU’s Department of Physics.
However.
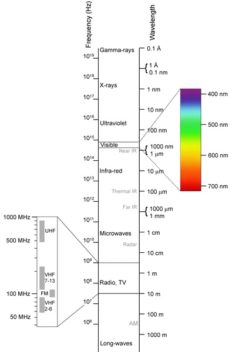
“Glass fibres are good up to a wavelength of about 3 microns. More than that, and they’re not so good,” she says.
And that is sometimes problematic.
Telecom uses the the near infrared part of the wave spectrum because it has the least loss of energy when passing through glass. But if we could utilize even longer wavelengths, the benefits would include better medical diagnoses and more precise environmental monitoring of airborne gas particles.
Longer wavelengths could also mean more space for media channels, since the competition is fierce for the wavelengths where free space transmission normally takes place now.
- You may also like: Why are you and I – and everything else – here?
Gallium antimonide
Optical glass fibres are not made of pure glass, but require a core with a bit of some other material to transmit signals. This is clearly quite complicated to achieve, and the methods have gradually been perfected over the last 50 years.
At NTNU, various research groups have been experimenting with optical fibres using a semiconductor core of silicon (Si) and gallium antimonide (GaSb) instead of small amounts of germanium oxide, which is used in silica fibres now.
Some of the researchers’ latest research findings have now been presented in Nature Communications. PhD candidate Seunghan Song is the first author of the article in the prestigious journal.
The article “describes a method for making optical fibres where part of the core that is gallium antimonide, which can emit infrared light. Then the fibre is laser treated to concentrate the antimonide,” says Gibson.
This process is carried at room temperature. The laser processing affects the properties of the core.
- You may also like: When 80 microns is enough
Cables and solar cells
Silicon is well known as the most commonly used material in solar panels. Along with oxygen, silicon is the most common material in glass and glass fibre cables as well. Gallium antimonide is less typical, although others have also used the same composition in optical instruments. But not in the same way.
With the new method, the gallium antimonide is initially distributed throughout the silicon. This is a simpler and cheaper method than others to grow crystals, and the technology offers many possible applications.
“Our results are first and foremost a step towards opening up larger portion of the electromagnetic wave spectrum for optical fibre transmission,” Gibson says.
Learning about the fundamental properties of the semiconductor materials in glass fibres allows us to make more efficient use of rare resources like gallium.
Source: Nature Communications. Laser restructuring and photoluminescence of glass-clad GaSb/Si-core optical fibres. S. Song, K. Lønsethagen, F. Laurell, T. W. Hawkins, J. Ballato, M. Fokine & U. J. Gibson. Published: 17 April 2019.